CSS position property comes of great use while positioning the elements on the web page. It comes with static, CSS sticky, absolute, relative, and fixed options. These values serve different purposes in defining the location of an element. Among them, position value absolute is something whose expertise will help you a lot in your web development career. It gives you more control over the elements and takes them out of the document’s normal flow.
An element with the position set as absolute can be positioned at a fixed location for all the situations you encounter in cross browser testing. However, the element will take the position relative to the first ancestor with the property set as absolute or relative. If no such element exists, the position takes reference from the root element, i.e., HTML.
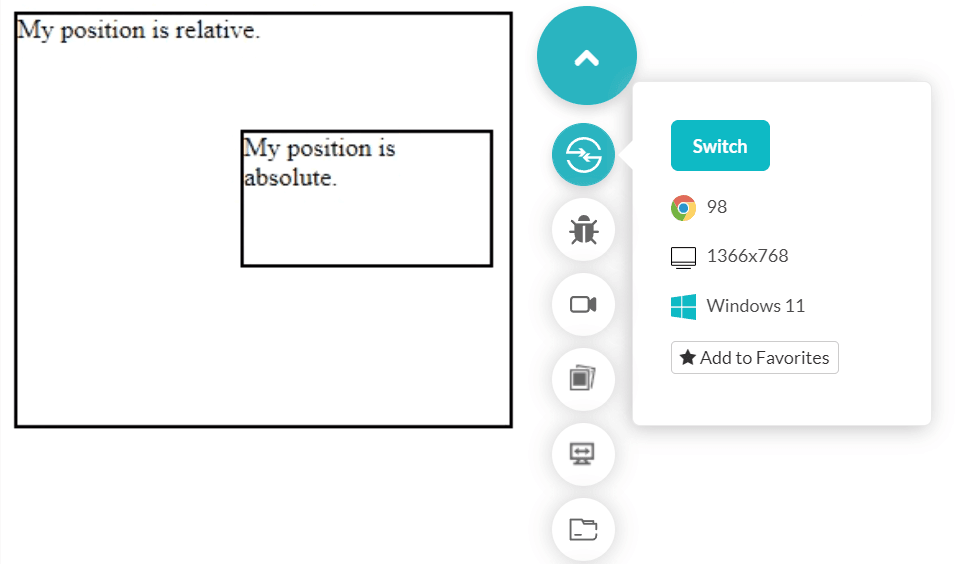
The following code places two div boxes with one as position: absolute.
The output is rendered as follows.
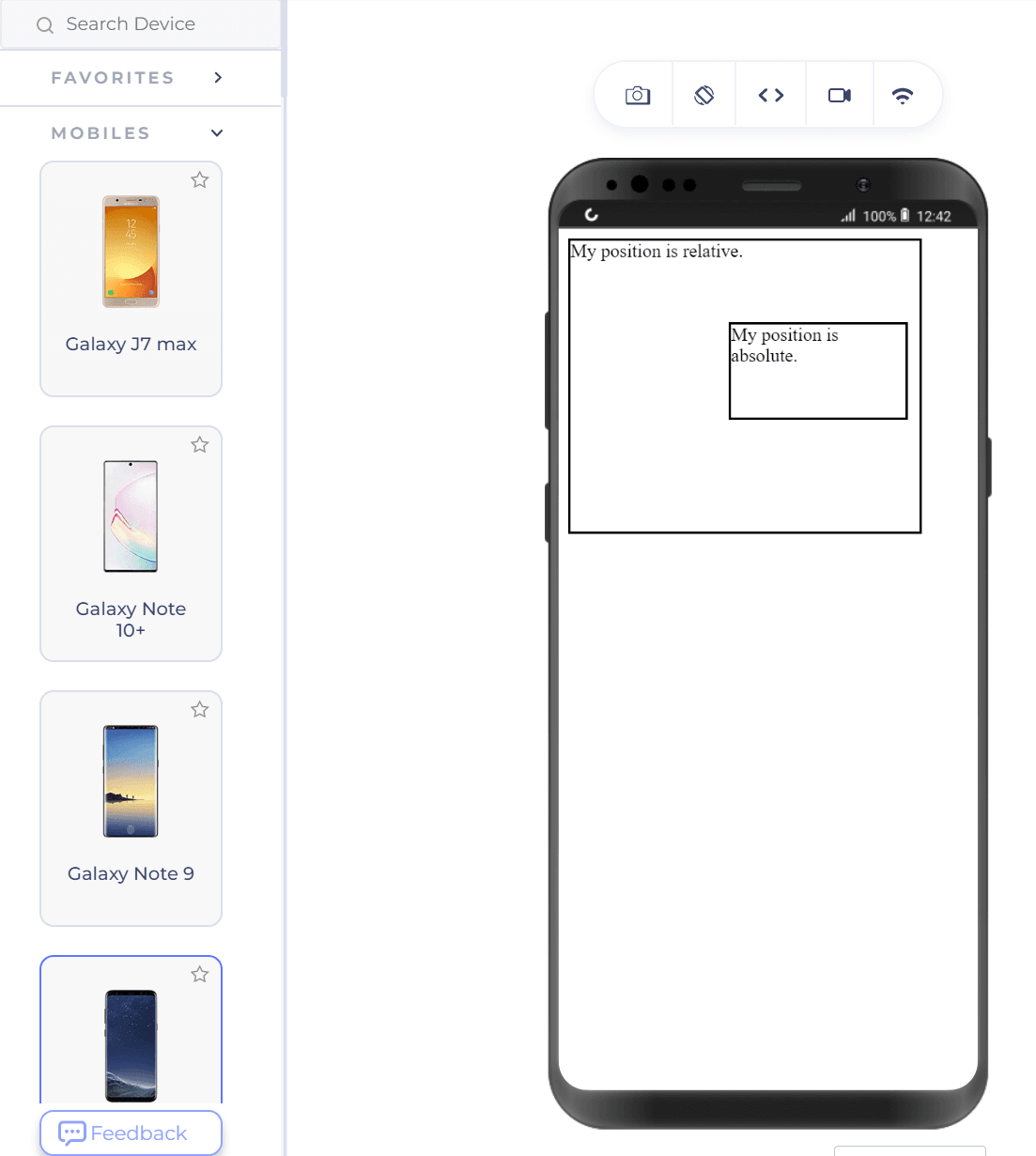
Output on mobile.
An element with the position set as absolute can be positioned at a fixed location for all the situations you encounter in cross browser testing. However, the element will take the position relative to the first ancestor with the property set as absolute or relative. If no such element exists, the position takes reference from the root element, i.e., HTML.
The following code places two div boxes with one as position: absolute.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Position Absolute</title>
</head>
<style>
div.relative {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
border: 2px solid #000000;
}
div.absolute {
position: absolute;
top: 70px;
right: 10px;
width: 150px;
height: 80px;
border: 2px solid #000000;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class = "relative">My position is relative.
<div class = "absolute">My position is absolute.</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>The output is rendered as follows.